架构详解
设计背景
先行者 Tengine
最早的 Tengine 是使用 C++ 分层设计的,编译采用 make,也就是嵌入系统常常采用的 makefile,编写之初支持的硬件是 CPU。可扩展性是 Tengine 和现在的 Lite 版本的设计核心,不仅仅是 Operator 能够很方便的通过注册宏扩展,各个主要模块也是扩展的。
推出 Tengine 发展一段时间后,市场反馈需要 Tengine 支持 MCU 和 VLIW 架构的 DSP;在一些项目中,编译工具链对 C++ 较新标准支持较差,甚至是没有 C++ 编译器,这就对 Tengine 的架构产生了新的要求。
在这种背景下,项目团队提出重新设计代号 Lite 的 Tengine 纯 C 语言的新主要分支,经过一段时间的开发后,后续项目陆续切换到 Tengine Lite 上。从能力上,Lite 和原分支是一样的。经过一段时间后,全部 Tengine 项目维护周期终结后,Tengine 分支将会进入存档冻结状态,不再维护。
继任者 Tengine Lite
“薪火相传 砥砺前行”,Tengine Lite 的早期版本主题设计和 Tengine 高度相似,较早的 Tengine Lite 版本注册机制依赖 GNU C 扩展,而 GNU C 扩展并不是标准 C 的内容。当社区呼唤需要扩展支持到非 GCC 系列的场景,如 Microsoft Visual Studio 上时,遇到了较多的困难。另一方面,纯 C 的设计使得 Tengine Lite 的入手难度较高,社区和项目反馈需要提高易用性,“Tengine 从入门到‘放弃’”的时间要“显著”缩短。
经过一段时间的磨合后,团队决定重新设计主要模块,重点是解决这几方面的问题。
架构设计
重新设计的设计目标之一是,采用纯 C 设计 Tengine 的 Lite 分支(以下简称 Tengine,不再强调 Lite 分支)最小 Runtime,复杂的功能和逻辑可以使用 C++ 开发。这样保持纯 C Runtime 在局限场景下优势的同时,使用 C++ 开发复杂模块,使注意力集中在开发算法本身上。
架构概览
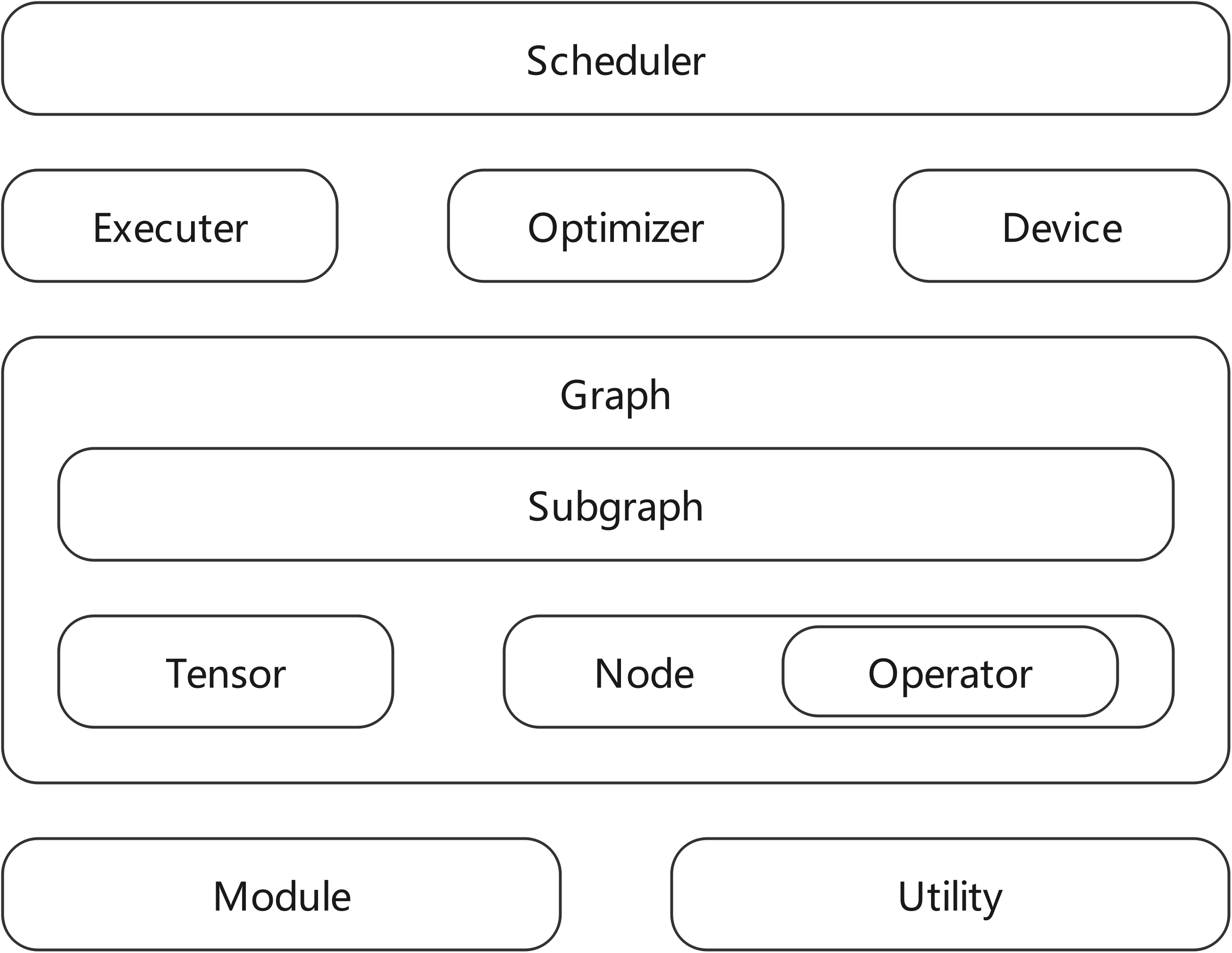
重要模块介绍
网络描述 graph 和相关结构体
source/graph 目录下是 Convolution Neural Network 的描述结构体和函数。
/*!
* @struct ir_graph_t
* @brief Abstract graph intermediate representation
*/
typedef struct graph
{
struct tensor** tensor_list; //!< the tensor list of a graph
struct node** node_list; //!< the node list of a graph
int16_t* input_nodes; //!< input nodes index array of a graph
int16_t* output_nodes; //!< output nodes index array of a graph
uint16_t tensor_num; //!< the count of all graph tensor
uint16_t node_num; //!< the count of all graph node
uint16_t input_num; //!< input nodes index count of a graph
uint16_t output_num; //!< input nodes index count of a graph
int8_t graph_layout; //!< the data layout of a graph
int8_t model_layout; //!< model layout of graph source model
int8_t model_format; //!< model format of graph source model
uint8_t status; //!< the status of graph
struct serializer* serializer; //!< serializer of graph
void* serializer_privacy; //!< privacy data of serializer
struct device* device; //!< assigned nn_device for this graph
void* device_privacy; //!< privacy data of device
struct attribute* attribute; //<! attribute of graph
struct vector* subgraph_list; //!< subgraph list of this graph
} ir_graph_t;
网络的主体 DAG 由 graph 和其中的 node 节点共同描述;全部需要的 node 在 node->node_list 中存储;node 主要描述了该节点的依赖 tensor 和 operator 情况。所有需要的 tensor 在 graph->tensor_list 中存储。graph->node_num 和 graph->tensor_num 分别描述了 graph 的 node 和 tensor 数量。数据(tensor) + 操作(operator)构成的节点(node)最后构成一个完整的图(graph),根据调度器(scheduler)模块的分配,形成一个完整的运行图运行在 CPU 设备(device)上,这也是典型的 CPU 跑 CNN 模型的应用场景。
/*!
* @struct ir_node_t
* @brief Abstract node intermediate representation
*/
typedef struct node
{
uint16_t index; //!< the index of a node
uint8_t dynamic_shape; //!< flag of dynamic shape
uint8_t input_num; //!< count of input tensor
uint8_t output_num; //!< count of output tensor
uint8_t node_type; //!< type of node: { input, output, intermediate }
int8_t subgraph_idx; //!< id of the owner subgraph
uint16_t* input_tensors; //!< id array of input tensor
uint16_t* output_tensors; //!< id array of output tensor
char* name; //!< name of a node
struct op op; //!< operator of a node
struct graph* graph; //!< pointer of the related graph
} ir_node_t;
node 是网络的节点,不同功能的 node 协助完成数据准备和计算的工作。node->input_tensors 和 node->output_tensors 分别描述了一个 node 的输入输出 tensor 的索引 index,结合 node->input_num 和 node->output_num 就可以完成节点的遍历。实际的 node 是存储在 graph->node_list 中的。
/*!
* @struct ir_tensor_t
* @brief Abstract tensor intermediate representation
*/
typedef struct tensor
{
uint16_t index; //!< the index of a tensor
int16_t producer; //!< node id, '-1' means no producer
int16_t consumer[TE_MAX_CONSUMER_NUM]; //!< consumer nodes array
uint8_t reshaped; //!< the tensor's shape has changed
uint8_t consumer_num; //!< count of consumer nodes
uint8_t tensor_type; //!< tensor_type: { const, input, var, dep }
uint8_t data_type; //!< data_type: { int8, uint8, fp32, fp16, int32 }
uint8_t dim_num; //!< count of dimensions
uint8_t elem_size; //!< size of single element
uint8_t subgraph_num; //!< count of all subgraph those will waiting this tensor ready
uint8_t free_host_mem; //!< should free host memory?
uint8_t internal_allocated; //!< how memory is allocated?
uint8_t layout; //!< tensor layout: { TENGINE_LAYOUT_NCHW, TENGINE_LAYOUT_NHWC }
uint16_t quant_param_num; //!< quantization dimension
uint32_t elem_num; //!< count of total elements
int dims[TE_MAX_SHAPE_DIM_NUM]; //!< shape dimensions
/*!
* @union anonymity data pointer
* @brief give useful pointer pointer
*/
union
{
void* data;
int8_t* i8;
uint8_t* u8;
float* f32;
uint16_t* f16;
int32_t* i32;
};
char* name; //!< tensor name
/*!
* @union anonymity quantization scale union
* @brief scale or its array
*/
union
{
float* scale_list;
float scale;
};
/*!
* @union anonymity quantization zero point union
* @brief zero point or its array
*/
union
{
int zero_point;
int* zp_list;
};
struct dev_mem* dev_mem;
uint8_t* subgraph_list; //!< subgraph index list of those subgraph will waiting this tensor ready
} ir_tensor_t;
tensor 是 node 完成功能的数据基础。tensor->dims 描述了 tensor 的 shape;tensor->quant_param_num, tensor->scale 或 tensor->scale_list,tensor->zero_point 或 tensor->zp_list 三者共同描述了 tensor 的量化情况,具体的数值类型由 tensor->data_type 描述。
当用户通过 API 对函数进行修改后,tensor->free_host_mem 和 tensor->internal_allocated 会进行变化,用来区分是由内部释放还是用户手动释放。
/*!
* @struct ir_op_t
* @brief Abstract operator intermediate representation
*/
typedef struct op
{
uint16_t type; //!< the type of a operator
uint8_t version; //!< the version of a operator
uint8_t same_shape; //!< the flag of weather the operator will keep shape
uint16_t param_size; //!< size of parameter memory buffer
void* param_mem; //!< parameter memory buffer
int (*infer_shape)(struct node*); //!< infer(or broadcast) the shape from input to output(s)
} ir_op_t;
operator 是 node 完成功能的行为基础。op->type 描述了类型,这是这个 op 的行为基础。
/*!
* @struct ir_subgraph_t
* @brief Abstract subgraph intermediate representation
*/
typedef struct subgraph
{
uint8_t index; //!< the index of a subgraph
uint8_t input_ready_count; //!< the count of all in ready input tensors
uint8_t input_wait_count; //!< the count of all out of ready input tensors
uint8_t input_num; //!< the count of input tensors
uint8_t output_num; //!< the count of output tensors
uint8_t status; //!< the execution status of subgraph
uint16_t node_num; //!< the count of nodes in subgraph
uint16_t* node_list; //!< all nodes index list of subgraph
uint16_t* input_tensor_list; //!< input tensors index list of subgraph
uint16_t* output_tensor_list; //!< output tensors index list of subgraph
struct graph* graph; //!< the pointer of the related graph
struct device* device; //!< the device which will the subgraph running on
void* device_graph; //!< the related device graph
} ir_subgraph_t;
subgraph 是设备有关的,一个 subgraph 只工作于一个单一 device。当网络的全部 node 完全运行于单一 device 时,subgraph 就包含全部 graph 中的 node。当运行于多 device 时,根据实际 device 的 operator 支持情况,划分不同的 node 到多个不同的 subgraph 中。最小的 subgraph 只包含一个 node 节点;最大的 subgraph 有全部的 node。
设备描述 device 和相关结构体
source/device 目录下是 Convolution Neural Network 的描述结构体和函数,子目录中是各种 device 的实现。其中 source/device/cpu 是 Tengine 支持的全部 CPU 的相关代码。
/*!
* @struct nn_device_t
* @brief Abstract neural network runnable device description struct
*/
typedef struct device
{
const char* name;
struct interface* interface; //!< device scheduler operation interface
struct allocator* allocator; //!< device allocation operation interface
struct optimizer* optimizer; //!< device optimizer operation interface
struct scheduler* scheduler; //!< device scheduler
void* privacy; //!< device privacy data
} ir_device_t;
device 是由嵌套的结构体构成的,结合描述了三类主要接口。关于详细细节和如何添加 device 还可以参考 扩展硬件后端 文档。
每当实现一个 device 的时候,都需要调用 int register_device(struct device* device); 函数,将 device 注册到 Tengine 中。运行时,可以通过 int add_context_device(context_t context, const char* dev_name); 和 int set_context_device(context_t context, const char* dev_name, const void* dev_option, size_t dev_opt_size); 设置需要使用的 device,对于带有 option 的 device,更推荐用后一个接口一并设置 option。比如,在 TensorRT device 中,需要初始化时指定多个 GPU 以及推理精度时特别有用。CPU device 被假设为总是可用。
模型解析 serializer 和相关结构体
/*!
* @struct serializer_t
* @brief Abstract serializer
*/
typedef struct serializer
{
const char* (*get_name)(struct serializer*);
//!< load model from file
int (*load_model)(struct serializer*, struct graph*, const char* fname, va_list ap);
//!< load model from memory
int (*load_mem)(struct serializer*, struct graph*, const void* addr, int size, va_list ap);
//!< unload model, free serializer and device related resource
int (*unload_graph)(struct serializer*, struct graph*, void* s_priv, void* dev_priv);
//!< interface exposed for register operator extension
int (*register_op_loader)(struct serializer*, int op_type, int op_ver, void* op_load_func, void* op_type_map_func, void* op_ver_map_func);
//!< interface exposed for register operator extension
int (*unregister_op_loader)(struct serializer*, int op_type, int op_ver, void* op_load_func);
//!< interface exposed for initialize serializer
int (*init)(struct serializer*);
//!< interface exposed for release serializer
int (*release)(struct serializer*);
} serializer_t;
支持新的模型格式解析,只需要填充并注册一个 serializer 即可完成。Tengine 正计划通过此模块将主流的模型支持增加进来。
模块注册
Tengine 能够工作有赖于注册的各个模块,这些注册接口和位置可以参考 source/module 目录下的相关代码。
static vector_t* internal_serializer_registry = NULL; //!< registry of model serializer
static vector_t* internal_device_registry = NULL; //!< registry of runnable neural network device
static vector_t* internal_op_method_registry = NULL; //!< registry of operators
static vector_t* internal_op_name_registry = NULL; //!< registry of operators name
从 source/module/module.c 中的 static struct vector 中可以知道, serializer,device 和 operaor 都被注册为 vector 中,在 module.h 中提供了注册和查找的函数。
/*!
* @brief Register a serializer.
*
* @param [in] serializer: The pointer to a struct of serializer.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int register_serializer(struct serializer* serializer);
/*!
* @brief Find the serializer via its name.
*
* @param [in] name: The name of serializer.
*
* @return The pointer of the serializer.
*/
struct serializer* find_serializer_via_name(const char* name);
/*!
* @brief Find the serializer via its registered index.
*
* @param [in] index: The index of serializer.
*
* @return The pointer of the serializer.
*/
struct serializer* find_serializer_via_index(int index);
/*!
* @brief Get count of all registered serializer.
*
* @return The count of registered serializer.
*/
int get_serializer_count();
/*!
* @brief Unregister a serializer.
*
* @param [in] serializer: The pointer to a struct of serializer.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int unregister_serializer(struct serializer* serializer);
/*!
* @brief Release all serializer.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int release_serializer_registry();
/*!
* @brief Register a device.
*
* @param [in] device: The pointer to a struct of device.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int register_device(struct device* device);
/*!
* @brief Find the device via its name.
*
* @param [in] name: The name of device.
*
* @return The pointer of the device.
*/
struct device* find_device_via_name(const char* name);
/*!
* @brief Find the default device.
*
* @return The pointer of the device.
*/
struct device* find_default_device();
/*!
* @brief Find the device via its registered index.
*
* @param [in] name: The index of device.
*
* @return The pointer of the device.
*/
struct device* find_device_via_index(int index);
/*!
* @brief Get count of all registered device.
*
* @return The count of registered device.
*/
int get_device_count();
/*!
* @brief Register a device.
*
* @param [in] device: The pointer to a struct of device.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int unregister_device(struct device* device);
/*!
* @brief Release all device.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int release_device_registry();
/*!
* @brief Register an operator method.
*
* @param [in] type: The type of an operator.
* @param [in] type: The name of an operator.
* @param [in] type: The method of an operator.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int register_op(int type, const char* name, struct method* method);
/*!
* @brief Find an operator method.
*
* @param [in] type: The type of an operator method.
* @param [in] version: The version of an operator method.
*
* @return The pointer of the method.
*/
struct method* find_op_method(int type, int version);
/*!
* @brief Find an operator method via its registered index.
*
* @param [in] index: The index of operator method.
*
* @return The pointer of the operator method.
*/
struct method* find_op_method_via_index(int index);
/*!
* @brief Find an operator name.
*
* @param [in] type: The type of an operator method.
*
* @return The char array of the method.
*/
const char* find_op_name(int type);
/*!
* @brief Get count of all registered operator method.
*
* @return The count of registered operator method.
*/
int get_op_method_count();
/*!
* @brief Register an operator.
*
* @param [in] type: The type of an operator method.
* @param [in] version: The version of an operator method.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int unregister_op(int type, int version);
/*!
* @brief Release all operator.
*
* @return statue value, 0 success, other value failure.
*/
int release_op_registry();
C 语言是没有 C++ 构造函数概念的,那么如果不做处理,就需要一套运行时注册和反注册的机制。在 Tengine v1.4 以后,注册的另一部分通过 CMake 完成。
通过一定规则扫描和收集到的文件,可以通过 cmake/registry.cmake 文件中添加的 GENERATE_REGISTER_HEADER_FILE(_REG_LEAD_STRING _DEL_LEAD_STRING _BACK_STRING _CONFIG_FILE _TARGET_FILE) 函数进行文件生成。
# generate needed registry
FUNCTION (GENERATE_REGISTER_HEADER_FILE _REG_LEAD_STRING _DEL_LEAD_STRING _BACK_STRING _CONFIG_FILE _TARGET_FILE)
SET (_BGN_NOTICE_STR "// code generation start\n")
SET (_END_NOTICE_STR "// code generation finish\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_DEF_STR "${_BGN_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_BGN_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_DEL_DEF_STR "${_BGN_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_BGN_NOTICE_STR}")
FOREACH (_VAR ${ARGN})
STRING(REGEX REPLACE ".+/(.+)\\..*" "\\1" _NAME ${_VAR})
SET (_REG_FUNC "${_REG_LEAD_STRING}${_NAME}${_BACK_STRING}()")
SET (_DEL_FUNC "${_DEL_LEAD_STRING}${_NAME}${_BACK_STRING}()")
SET (_GEN_REG_DEF_STR "${_GEN_REG_DEF_STR}extern int ${_REG_FUNC};\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} ret = ${_REG_FUNC};\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} if(0 != ret)\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} {\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} TLOG_ERR(\"Tengine FATAL: Call %s failed(%d).\\n\", \"${_REG_FUNC}\", ret);\n")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} }\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_DEF_STR "${_GEN_DEL_DEF_STR}extern int ${_DEL_FUNC};\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} ret = ${_DEL_FUNC};\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} if(0 != ret)\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} {\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} TLOG_ERR(\"Tengine FATAL: Call %s failed(%d).\\n\", \"${_REG_FUNC}\", ret);\n")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} }\n")
ENDFOREACH()
SET (_GEN_REG_DEF_STR "${_GEN_REG_DEF_STR}${_END_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_REG_CAL_STR "${_GEN_REG_CAL_STR} ${_END_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_DEL_DEF_STR "${_GEN_DEL_DEF_STR}${_END_NOTICE_STR}")
SET (_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR "${_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR} ${_END_NOTICE_STR}")
CONFIGURE_FILE(${_CONFIG_FILE} ${_TARGET_FILE})
ENDFUNCTION()
这个函数的核心就是根据输入的文件列表,产生两个字符串 _GEN_REG_CAL_STR 和 _GEN_DEL_CAL_STR,这两个字符串将会在生成过程 CONFIGURE_FILE(${_CONFIG_FILE} ${_TARGET_FILE}) 中,替换掉 header_name.h.in 中的 @_GEN_REG_CAL_STR@ 和 @_GEN_DEL_CAL_STR@ 字符串部分,分别完成函数的声明、注册函数的调用、反注册函数的调用,生成的文件一般会保存在 ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR} 中的对应位置,这由函数的 _TARGET_FILE 指定。
以 serializer 的 CMakeLists.txt 为例,生成函数调用如下:
# generate all serializer
GENERATE_REGISTER_HEADER_FILE("register_" "unregister_" "" "${_SRL_SRC_ROOT}/register.h.in" "${_SRL_BIN_ROOT}/register.h" "${_SRL_TM2_SRL_SOURCE}")
这样就完成了配置过程,生成的头文件进一步的在后续的编译过程中发挥作用。当用户使用静态分析功能的 IDE 审阅代码时,由于相关头文件没有生成,所以可能会发生无法跳转的情况。经过编译配置的 Microsoft Visual Studio Code 等在打开文件夹后,会启动 CMake 进行配置和生成,这时的头文件就会生成,也能进行跳转了。其他 Microsoft Visual Studio 或 JetBrains CLion 等 IDE 也可以完成配置和生成过程,推荐使用。